Order Information
Raji-Luc
 Ref. Zhang, D.K.Y., Adu-Berchie, K., Iyer, S. et al. Enhancing CAR-T cell functionality in a patient-specific manner. Nat Commun 14, 506 (2023).
Ref. Zhang, D.K.Y., Adu-Berchie, K., Iyer, S. et al. Enhancing CAR-T cell functionality in a patient-specific manner. Nat Commun 14, 506 (2023).
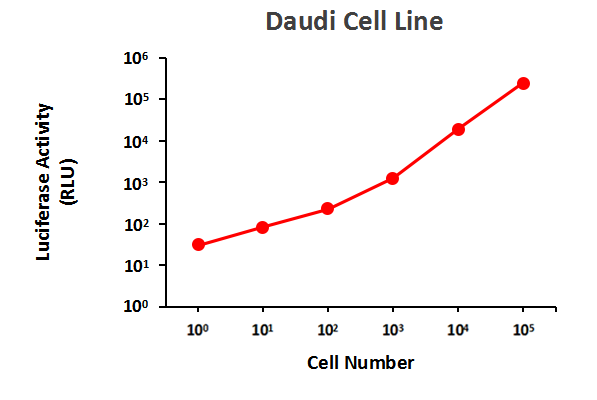
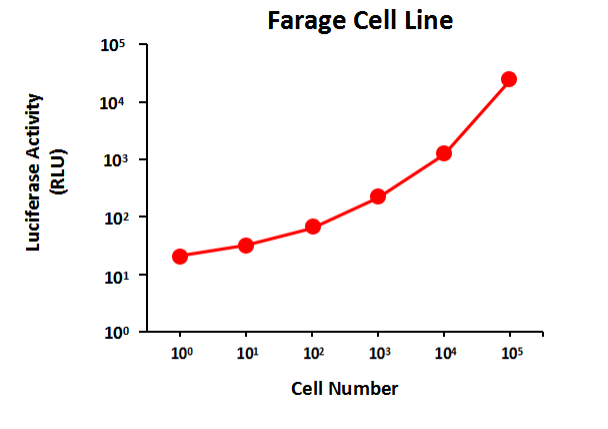
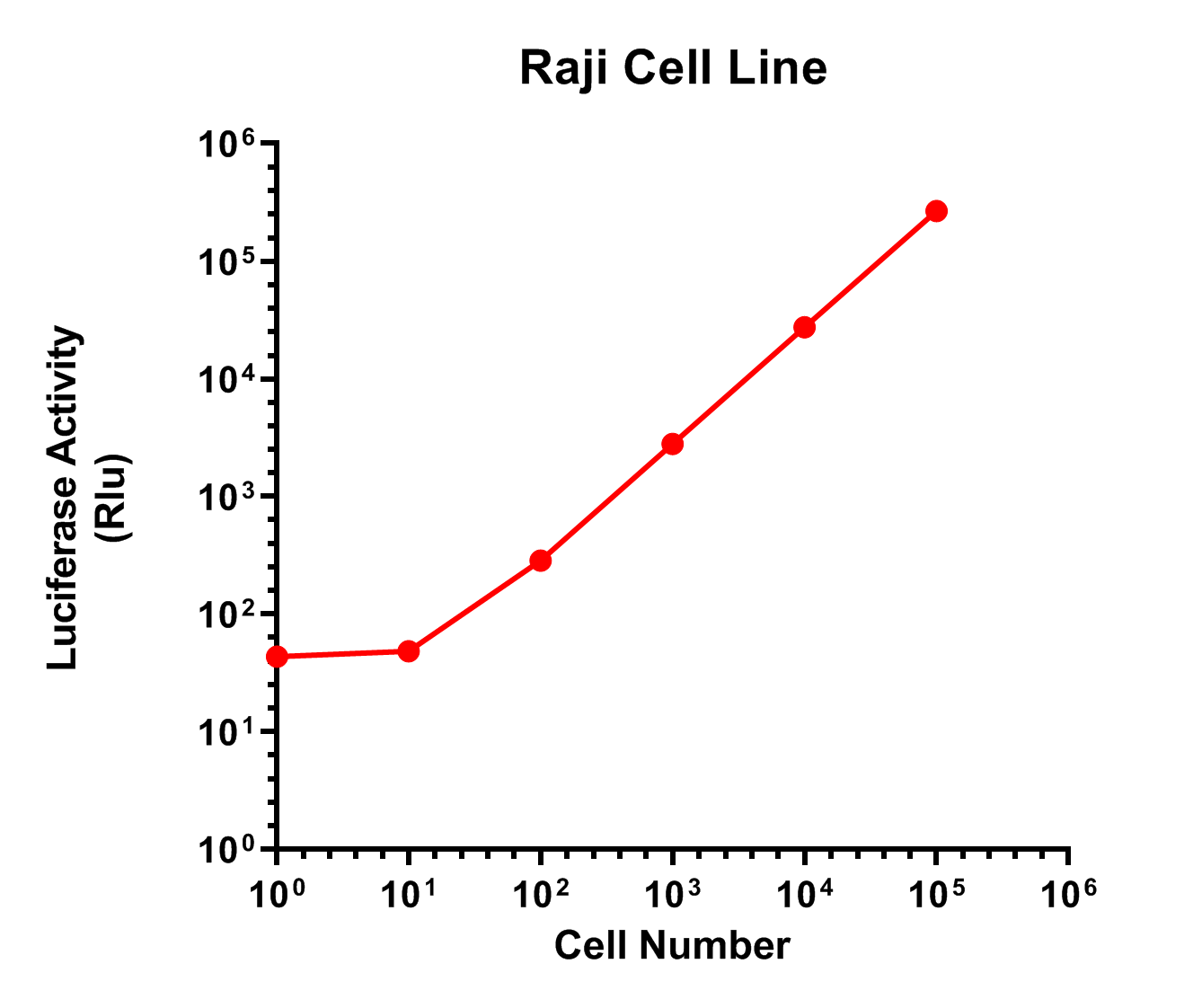 Serial dilutions of Raji-Luc cells were plated into a 96 well plate (white well). The luciferase activity was tested using GeneCopoeia™ Luc-Pair™ Firefly Luciferase HS Assay Kit (Cat. No. LF007). High expression of Luciferase activity was detected in this cell line.
Serial dilutions of Raji-Luc cells were plated into a 96 well plate (white well). The luciferase activity was tested using GeneCopoeia™ Luc-Pair™ Firefly Luciferase HS Assay Kit (Cat. No. LF007). High expression of Luciferase activity was detected in this cell line.
CAR-T target luciferase-labeled Raji cell line
Established from tumour cells of a Burkitt’s lymphoma patient, Raji cells constitutively express the B-cell antigens CD19, CD20, and CD22 and can be used to evaluate cancer-targeted immunotherapies such as CAR-T cells. The luciferase-labeled Raji cancer cell line was modified from the Raji wild-type cell line to express firefly luciferase stably. Raji-Luc cell line did not differ significantly from the wild-type cells in appearance, and trended similarly to the wild-type Raji cell line in terms of tumourigenicity. High expression of luciferase activity was detected in this cell line. Raji-Luc cell line is an excellent target for CAR-T or NK cells targeting CD19, CD20 or CD22. The luciferase reporter gene produces a signal that is proportional to the number of Raji cells, helping to quantify how well it kills Raji cells when co-cultured with CAR-T or NK cells.Case study
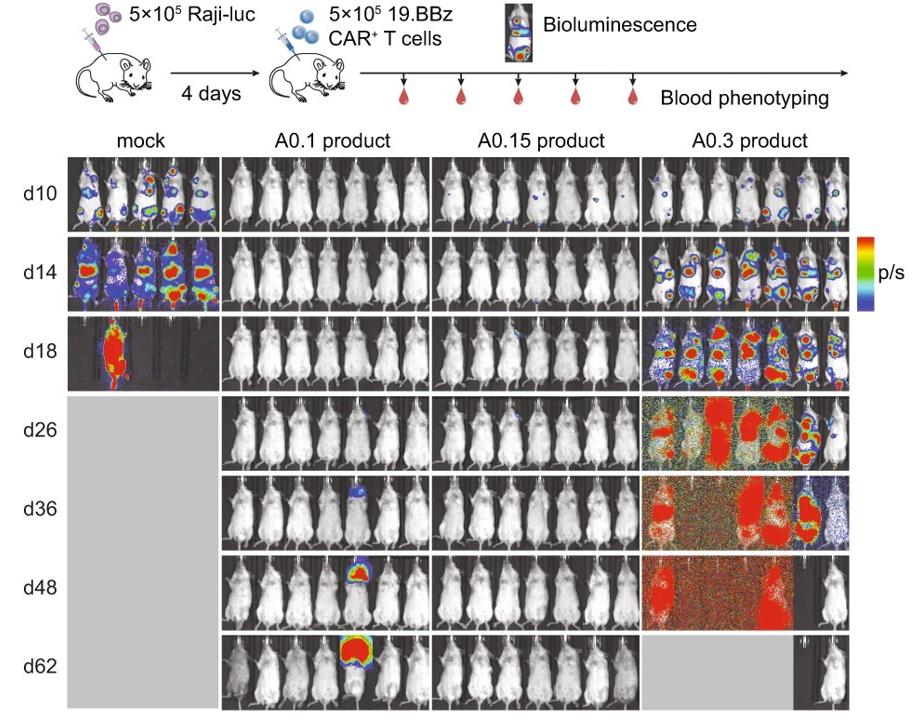
The luciferase-labeled Raji cancer cell line naturally expresses high levels of CD19, which can be used as a target cancer cell for an in vitro killing assay by CD19 CAR-T cells and is expected to also work for CD20 CAR-T cells. Zhang, D.K.Y. et al. tested the efficacy of three CAR-T cell products using CD19-expressing Raji-luc cells in a disseminated xenograft model of Burkitt’s lymphoma. The level of fluorescence intensity of Raji-luc cells in vivo reflects the proliferation and distribution of tumour cells in the animal. Ref. Zhang, D.K.Y., Adu-Berchie, K., Iyer, S. et al. Enhancing CAR-T cell functionality in a patient-specific manner. Nat Commun 14, 506 (2023).
Ref. Zhang, D.K.Y., Adu-Berchie, K., Iyer, S. et al. Enhancing CAR-T cell functionality in a patient-specific manner. Nat Commun 14, 506 (2023).
Performance data
 Serial dilutions of Raji-Luc cells were plated into a 96 well plate (white well). The luciferase activity was tested using GeneCopoeia™ Luc-Pair™ Firefly Luciferase HS Assay Kit (Cat. No. LF007). High expression of Luciferase activity was detected in this cell line.
Serial dilutions of Raji-Luc cells were plated into a 96 well plate (white well). The luciferase activity was tested using GeneCopoeia™ Luc-Pair™ Firefly Luciferase HS Assay Kit (Cat. No. LF007). High expression of Luciferase activity was detected in this cell line.