Introduction
OmicsLink
™ shRNA clone collections include lentiviral and non-viral vector-based shRNA constructs against genome-wide human, mouse and rat genes. shRNA of varying lengths (19 to 29 bases) were designed using a proprietary algorithm to make shRNA expression constructs that have high knockdown efficiency with minimal off-target effect.
Guaranteed shRNA knockdown
A set of three expression constructs and a scrambled control is offered against every target gene with the guarantee that at least one of the three will have a knockdown effect of 70% or more on corresponding gene expression as determined by qRT-PCR, otherwise the constructs will be replaced one time free of charge. For more about our guaranteed shRNA knockdown, refer to
warranty and cancellation policy here.
All cell types covered
Lentiviral and non-viral vector options allow the transfection or transduction of shRNA into difficult-to-transfect cells as well as more conventional cell lines.
Promoters of your choice
shRNA is driven by pol III promoters (H1, U6) or pol II promoters (CMV, EF1a, CAG and CBh), both with great knockdown efficiency.
Request a quote for pol II promoter-driven shRNA lentivirus or AAV services.
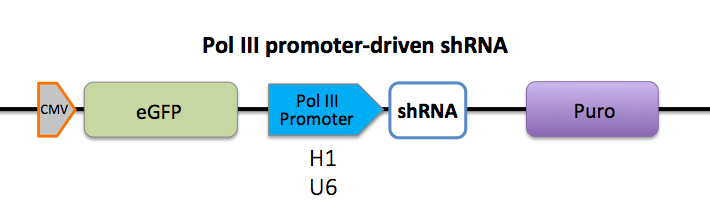
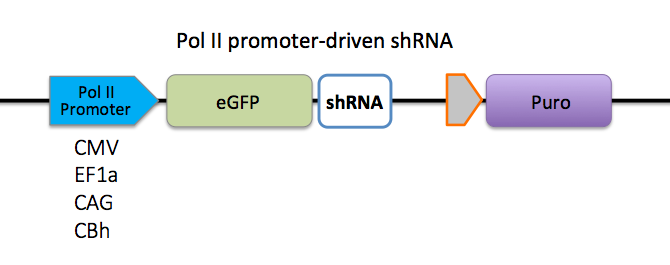
Multiple delivery formats
shRNAs are delivered as 3 individual constructs of 5 µg purified plasmid and a separate scrambled control plasmid.
Lentivirus and
AAV for shRNA are also available.
Markers and reporters
Vectors with mCherry or eGFP reporter genes for monitoring transfection or transduction efficiencies. Stable cell selection with puromycin marker.
Fully sequenced expression cassettes
Expression cassettes of all shRNA clones are fully sequenced including the promoter, sense and antisense target sequences, hairpin, terminator, and other linker sequences.
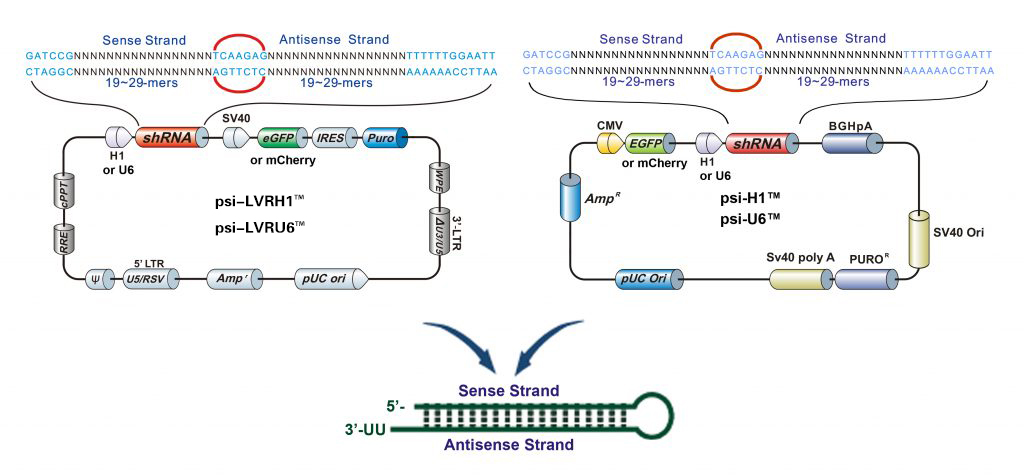
Figure 1. Lentiviral and non-viral expression vector-based shRNA clones
Applications
Single gene down-regulation — The knocking down (KD) effect of the shRNA clones for a single gene can be studied and compared with that of a scrambled nucleotide control clone which is included for free with every shRNA clone order.
Pathway analysis — Genes have been grouped into various signal transduction, metabolic, and disease pathways and associations, as well as gene families and groups. By arraying the shRNA clones of known pathway(s) in 96 or 384 well plates, the role for a group of genes can be studied in a pathway.
Validation studies — The OmicsLink™ expression ready ORF cDNA clones together with the same ORF clones that contain silent mutations in shRNA target sequence regions can be used for shRNA validation studies and gene/protein functional rescue studies for genes/proteins targeted by corresponding shRNA.
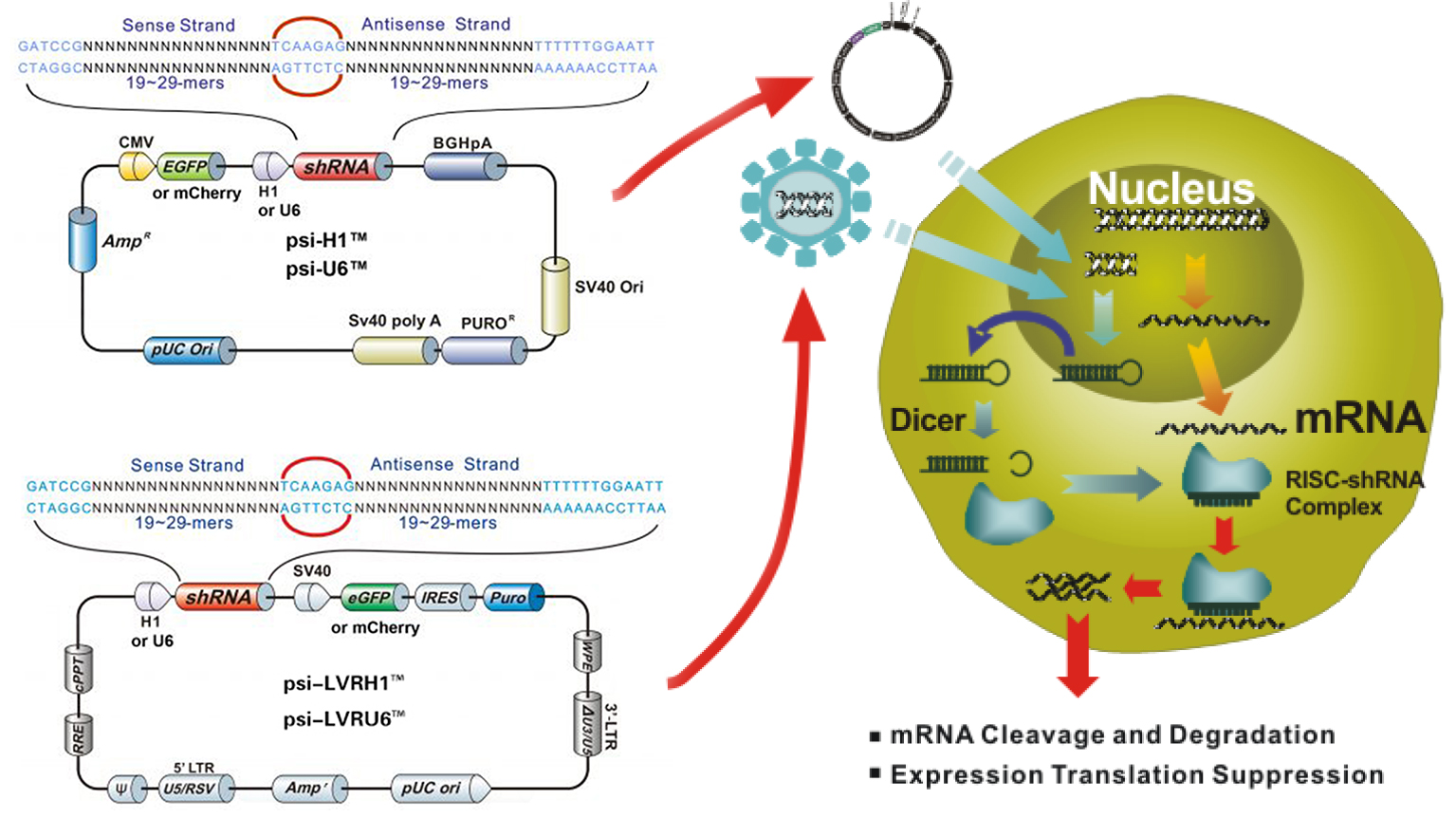
Figure 2. Mechanism of shRNA vector-mediated gene silencing
Measurement of knockdown (KD) effect by vector-based shRNA clones
|
|
qRT-PCR — Targeting of the corresponding mRNA by a shRNA expression cassette leads to cleavage and degradation of the mRNA and possible subsequent reduction of protein expression. qRT-PCR is recommended as the first step in measuring KD effect. Validated qRT-PCR primers for corresponding target genes (and any other published transcripts) are also available.
Western blot analysis — Protein down-regulation is required in most cases for gene KD studies which can be assessed by western blot analysis.
Functional assays — The shRNA knockdown effect can be studied by end-point biological and biochemical assays such as cell proliferation, colony formation, cell cycle analysis, and migration based on the potential role played by each gene /protein.
Functional assays by a reporter gene/protein — Alternatively, when the endogenous transcript level of gene of interest is low and/or when qRT-PCR and western blot analysis is not feasible or possible, KD effect can be measured by co-transduction of shRNA clone with an expression clone plasmid which is transcribed into a chimeric mRNA transcript consisting of a reporter gene and the target gene ORF. The reporter gene encodes a reporter protein enzyme that can be used in functional assays. The destruction of the target gene mRNA by targeting shRNA results in the degradation of the reporter gene and, therefore, translation reduction of reporter protein enzyme.
To Order
Pre-designed shRNA clones sets
Search over 24,000 human, 20,000 mouse, and 10,000 rat pre-designed shRNA clone sets in your choice of the vector.

shRNA lentivirus
GeneCopoeia offers shRNA lentivirus as a custom service.
Request a quote for lentivirus production services.


shRNA AAV
GeneCopoeia offers shRNA AAV as a custom service.
Contact us for a quote for AAV production services.


Custom shRNA clone services

Related Products
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions: shRNA clone sets
Answer: All you need to do is go to the
shRNA clones search page, search for your gene, and then choose the appropriate clones that will work for your system. If you have any custom requirements, then you will need to
contact us and, after determining what you need, we will send you a custom quote.
Answer: GeneCopoeia provides a set containing 3 individual shRNA constructs and a scrambled control. Each clone is provided as of 5 µg purified plasmid. A datasheet containing information for each clone, vector and restriction enzyme sites is available for
download on our website. You will need a GeneCopoeia account, your sales order number, and your catalog number(s) in order to download the datasheet.
Answer: GeneCopoeia guarantees that the shRNA sequences in the expression cassettes are identical to the target gene. If none of the three constructs produce a 70% or greater knockdown efficiency as determined by qRT-PCR, and the inefficiency is caused by a flaw in our construct design, then we will provide another set of three new clones targeting the specific gene free of charge.
Answer: We offer both promoters so customers can choose based on their preference. U6 is the stronger promoter, however, because it is stronger there is a greater chance of causing off-targeting effects or cellular toxicity. In most cases either promoter should be fine to use, however, there are tissue and cell specificities associated with each promoter. We recommend doing a literature search to see what other researchers have used for the particular cells you are working with.
Answer: Yes, Stbl3 is recommended.
Answer: You should measure the knockdown efficiency when the transfection efficiency is greater than 80%. The reporter gene in the vector is used to monitor transfection efficiency. Alternatively, if the transfection efficiency of your cell line is low, you can order the lentiviral versions of your clones and transduce your cells with the lentiviruses. RNA can be harvested from transfected cells and used in quantitative RT-PCR to estimate the reduction in gene expression. Western blot is recommended over qPCR to evaluate the silencing effect of the shRNA construct(s). Gene expression levels from cells transfected with a scrambled control clone must be compared with the shRNA transfected samples.
Answer: Factors influencing transfection efficiency include 1) The quality of the plasmid DNA; 2) The condition of the cells; 3) The quality, condition, or age of your transfection reagents and plasmids; 4) The cell density at the time of transfection; and 5) The contact time between cells and the DNA/transfection reagent complex.
Answer: The scrambled control clone is constructed by cloning a scrambled sequence (one that does not match any genomic sequences) into shRNA vectors. It serves as a negative control to eliminate the potential non-specific effect induced by expression of the plasmid.
Answer: We strongly recommend performing a kill curve on each batch of cells to determine the optimal puromycin concentration.










