Introduction
The AviTag™ is a popular fusion tag due to its powerful and versatile properties. Fused to your protein, the AviTag™ provides a multi-functional system useful for many applications including:
- Expression
- Imaging
- Detection
|
- Localization
- Isolation
- Immobilization
|
Technology
The AviTag™ technology is based on the biotinylation of AviTag™ by biotin ligase in vitro or in vivo and on the specific and reversible binding of avidin or streptavidin to biotin for immobilizing, purifying and visualizing proteins. See applications of AviTag technology.
Combined with OmicsLink™ expression-ready clones
GeneCopoeia offers the AviTag™ technology in a wide range of expression vectors. For example, it has been combined with the IRES (Internal Ribosome Entry Site) element and the SUMO, 6xHIS and a variety of other tags.See the complete list of AviTag expression vectors here.
The AviTag with T7- or CMV-driven promoters is available for more than 20,000 human and 15,000 mouse genes.
|
|
Specific
Biotinylation of recombinant protein bearing the AviTag is highly specific. In the presence of biotin and ATP, biotin ligase catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the 15-aa AviTag peptide.
Biotinylated proteins in nature are extremely rare making the chances for cross reactions, especially when compared to antibodies, very low.
GeneCopoeia also offers biotin ligase, biotinylation strains and Avitag vectors.
Learn more about biotin ligase and biotinylation strains.

|
Figure1. OmicsLink ORF cDNA expression clones with N- and C-terminus AviTag in various mammalian vector systems. |
Advantages over chemical biotin-labeling
- During chemical biotin-labeling the protein can become inactivated due to random biotinylation of the protein surface by the attachment of biotin to protein catalytic or binding domains. With Avi-Tag, virtually any protein can be easily and efficiently biotinylated in vivo or in vitro using the single, unique AviTag site.
- Biotinylation using Avi-Tag is performed enzymatically resulting in gentle reaction conditions and highly specific labeling.
- Biotin-AviTag has 15 amino acids, which is a fifth of the bulk of alternative biotinylation tag sequences that are over 85 amino acid residues long; an important consideration if steric conflicts are to be minimized.
|
How it works
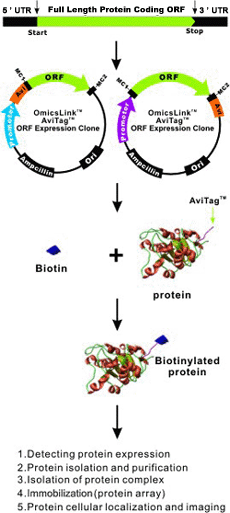
|
Applications and Data
Applications of cDNA clones with AviTag and fusion proteins
- Use immobilized AviTag-fusion proteins for high-throughput screening and protein-protein interaction studies using surface plasmon resonance.
- Purify AviTag-fusion proteins using monomeric avidin.
- Visualize AviTag-fusion proteins using avidin or streptavidin conjugates with western blots and MHC-tetramers for staining and sorting T cells.
Rigorous quality control and assurance process
All ORFs in OmicsLink clone collection were generated from sequence validated full-length cDNA clones or high-quality human tissue cDNA libraries to construct expression-ready clones.
Once the clone is constructed, GeneCopoeia follows additional quality control process to ensure the right clone is delivered to our customers.
- All ORFs are fully sequenced.
- PCR amplification and size validation
- Enzyme digestion check of the integrity of whole plasmid
Example of in vitro biotinylation of AviTag recombinant proteins
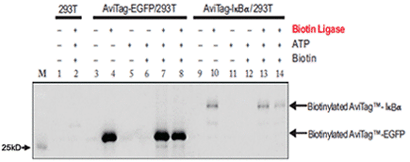
Figure2. Extracts from 293T cells transfected with the AviTag eGFP or AviTag-IkBαexpression plasmid and untransfected controls were mixed with purified biotin ligase, biotin (50M) and ATP (10mM) as indicated in the figure. After incubation at 30.C (lanes 1-7, 9-13) or 4.C (lanes 8, 14) for 30 minutes, the mixtures were resolved by SDS-PAGE. Biotinylated proteins were visualized on a western blot with streptavidin-HRP conjugate and chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce).
Example of in vivo biotinylation of AviTag recombinant proteins
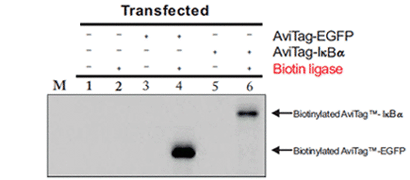
Figure3. AviTag-eGFP or AviTag- IkBα expression plasmids were transfected into 293T cells alone or with co-transfected biotin ligase. Lysates were prepared 13 hours. Extracts from after transfection and resolved on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel. Biotinylated proteins were visualized on a western blot with streptavidin-HRP conjugate and chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce).
Example of precipitation of biotinylated AviTag recombinant proteins with streptavidin beads
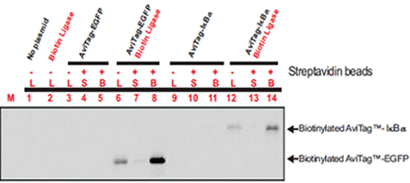
Figure4. 293T cells were transfected with different combinations of AviTag expression plasmids and biotin ligase, as indicated in the figure. Lysates were prepared 24 hours after transfection and incubated with streptavidin beads for 8 hours. Suspensions were centrifuged and pelleted beads were washed 3 times. Cell lysates (L), supernatants (S) and pelleted biotinylated protein bound to streptavidin beads (B) were resolved by SDS-PAGE. Biotinylated proteins were visualized on a western blot with streptavidin-HRP conjugate and chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce).