Introduction
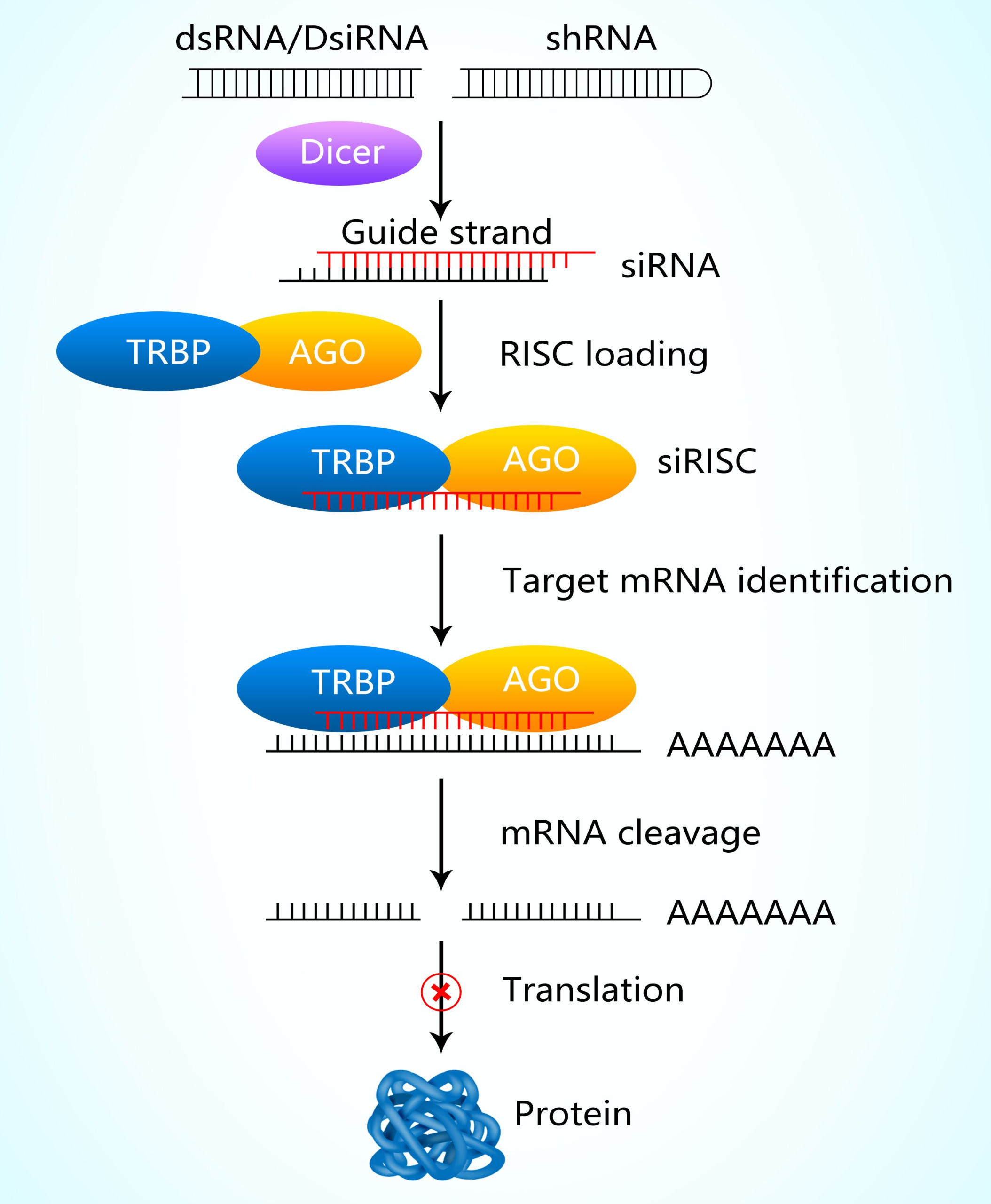
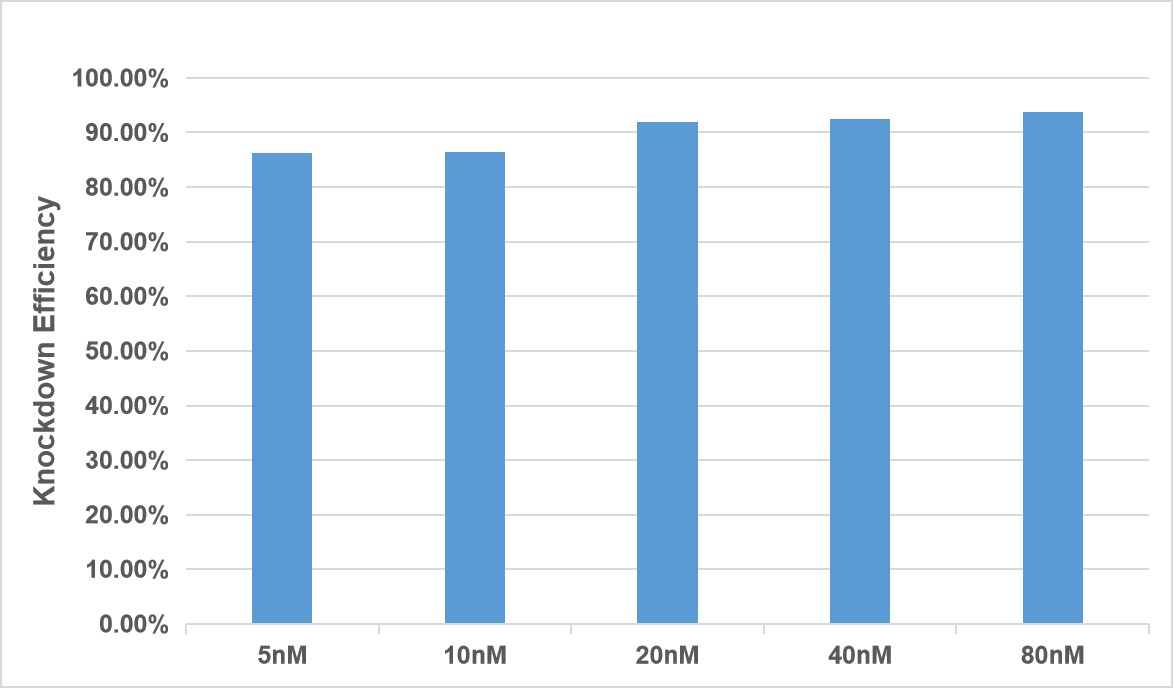 Figure 2. GAPDH-siRNA at different concentrations of 5nM/10nM/20nM/40nM/80nM was transfected into H1299 cells in 24-well plates. After 24h, qPCR was used to quantitatively detect the knockdown efficiency of the GAPDH gene.
Figure 2. GAPDH-siRNA at different concentrations of 5nM/10nM/20nM/40nM/80nM was transfected into H1299 cells in 24-well plates. After 24h, qPCR was used to quantitatively detect the knockdown efficiency of the GAPDH gene.
Small interfering RNA (siRNA), also known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a type of double-stranded RNA molecules that function within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It inhibits translation, hence inhibiting the expression of certain genes with complementary nucleotide sequences, by degrading mRNA after transcription. GeneCopoeia provides siRNA oligo design and synthesis services, and all siRNA products are purified by standard HPLC.
Mechanism of action
Exogenous or endogenous dsRNA enters the cytoplasm and is cleaved into siRNA by the action of the ribonuclease Dicer. RNA-binding protein (TRBP), Argonaute 2 protein (Ago2 protein), Dicer, and siRNA combine to form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Ago2 protein accurately recognizes and binds to the antisense strand of siRNA (Guide strand). The antisense strand of siRNA recognizes the complementary mRNA and cleaves the target mRNA under the action of the endonuclease in RISC, thereby interfering with gene expression.

Figure 1. Mechanism of action of siRNA
Performance data
 Figure 2. GAPDH-siRNA at different concentrations of 5nM/10nM/20nM/40nM/80nM was transfected into H1299 cells in 24-well plates. After 24h, qPCR was used to quantitatively detect the knockdown efficiency of the GAPDH gene.
Figure 2. GAPDH-siRNA at different concentrations of 5nM/10nM/20nM/40nM/80nM was transfected into H1299 cells in 24-well plates. After 24h, qPCR was used to quantitatively detect the knockdown efficiency of the GAPDH gene.

