 |
Ed Davis, Ph.D. |
Abstract
Genome Editing-the ability to make specific changes at targeted genomic sites-is fundamentally important to researchers in biology and medicine (Bogdanove & Voytas, 2011; van der Oost, et al., 2013). Two genome editing technologies have emerged recently that exploit bacterial systems for plant pathogenesis or adaptive immunity: TALEN (Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases) and CRISPR (Clustered, Regularly Interspaced, Short Palindromic Repeats), respectively. Both TALEN and CRISPR use endonucleases that initiate double-strand breaks (DSBs) at virtually any genomic target sequence, and are used for many applications, including gene knockout, transgene knock-in, gene tagging, and correction of genetic defects. In this Review, we discuss and compare genome editing technologies, applications for genome editing using published case studies, and how GeneCopoeia genome editing technologies and services can accelerate your research.
Introduction
What is Genome Editing?In the strictest sense, genome editing means making stable, permanent, and heritable changes to the genetic code, to accomplish many potential goals. The process begins with stimulation of a DSB at the target site. DSBs are lethal if left unrepaired, so eukaryotic cells have several mechanisms in response (Figure 1). The first is homologous recombination (HR), whereby cells use a homologous copy of the broken chromosome as a repair template. HR is a relatively error-free process. The template is normally the sister chromatid during G2 in mitosis, but can also come from a DNA fragment introduced exogenously, which can mediate a “knock in” of desired DNA sequences to the target site.
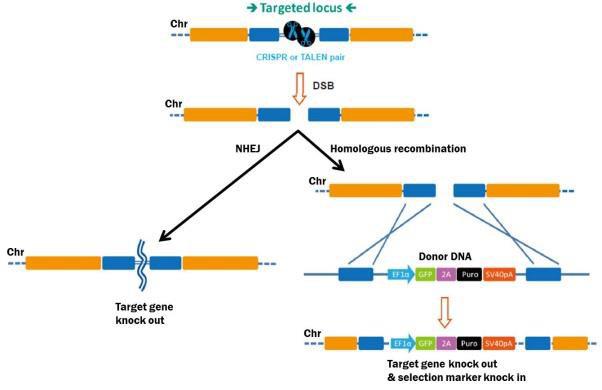
|
Figure 1. Pathways for repair of DSBs induced by genome editing tools. Left: Non-homologous end joining. Right: HR in the presence of a donor template. The second major mechanism for DSB repair is nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), which occurs when no homologous template is available. NHEJ is simply the re-connection of the broken chromosome ends. However, NHEJ is error-prone, and frequently leads to small insertions or deletions (“indels”) at the break site. Indels can disrupt a gene by causing frame shifts, and, therefore, gene knockouts. |
Genome Editing tools can also be used for non-permanent changes in gene expression, by adapting them as fusions to either transcriptional activators or repressors. While this is a popular application of these tools, it will not be covered in this review.
RNAi-mediated knockdown is the most common strategy for ablating gene function in higher eukaryotes. However, there are a few key differences between RNAi and genome editing. First, RNAi does not completely shut off the gene (Ketting, 2013). Rather, gene expression is down-regulated post- transcriptionally, without changing the genetic code (Mittal, 2004). Some functional RNA or protein remains and is translated. So, the RNAi strategy is a “knockdown”. Gene function is reduced, not eliminated. In genome editing, on the other hand, the genetic code is changed, and attenuation of gene expression is usually complete, leading to a “knockout”. The decision on whether to use RNAi or genome editing for attenuating gene expression depends on the goals of the experiment. (Table 1).
| Method | Knock down | Knock out | genetic code | Change expression level | Clone isolation required |
| RNAi (shRNA, siRNA) | √ | √ | |||
| Genome editing (TALEN, CRISPR) | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Genome editing technologies
TALENIn nature, TALs are DNA binding proteins from bacteria that infect plants (Bogdanove & Voytas, 2011). DNA binding is mediated by 34 bp amino acid repeats, which differ at amino acids 12 and 13. These “repeat variable diresidues”, or RVDs, facilitate TALEN DNA binding specificity. Each RVD binds one nucleotide, and a DNA binding code has been determined (Figure 2).
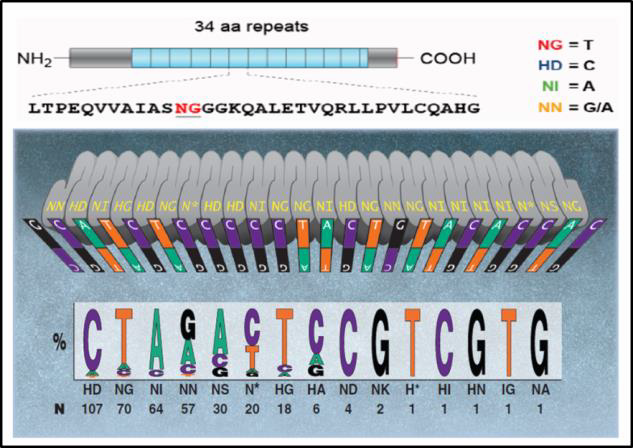
| Figure 2. DNA binding code for TALENs. Adapted from Bogdanove & Voytas (2011).
TALENs consist of two DNA binding proteins. Each is fused to one domain of the FokI restriction endonuclease, and recognizes 17-18 bp of target sequence. FokI requires dimerization for activity, so when two properly designed TALs-on opposite sides of the intended break site and on opposite strands,with approximately 18 nucleotides in between-come together, FokI cuts the DNA. The resulting DSB is repaired by either NHEJ or HR as described above. |
CRISPR’s mechanism differs from TALEN, with the same end result. CRISPR’s natural function is to destroy phages that invade bacteria for adaptive immunity. For genome editing, the S. pyogenes Cas9 nuclease is inactive until it binds to a single guide RNA (sgRNA). An sgRNA contains a 20 nucleotide genomic sequence. The Cas9-sgRNA complex recognizes this sequence in the genome when it is immediately followed by a 5’ N-G-G 3’ “PAM” site. Upon recognition, the sgRNA hybridizes with the strand opposite the PAM, and Cas9 creates a DSB (Figure 3).
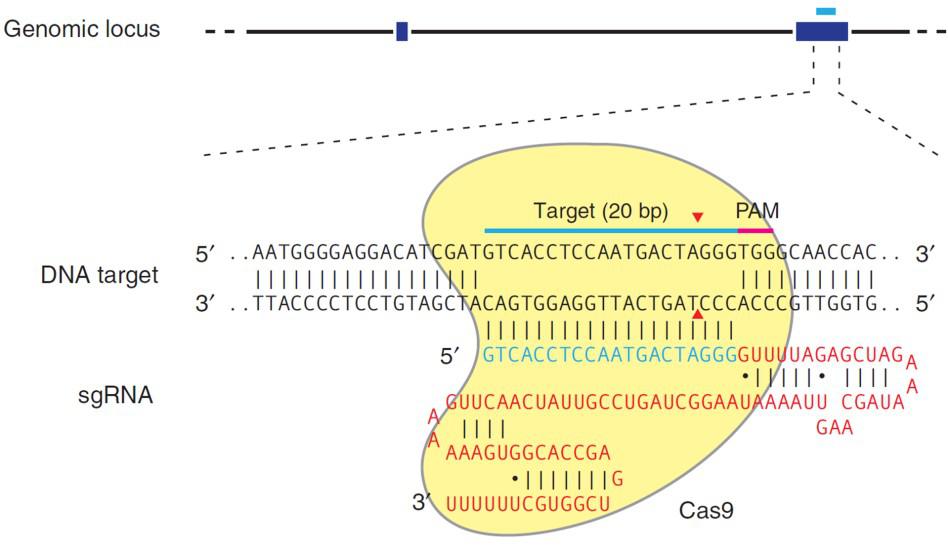
| Figure 3. Recruitment of Cas9 to a target locus by an sgRNA. Red sequences, sgRNA scaffolding. Blue, target sequence. The PAM is indicated by the red bar. The sgRNA target sequence binds to the strand opposite the PAM site. Cas9 cuts both sDNA strands between the third and fourth nucleotide 5’ of the PAM. Red arrows: Position of the DNA strand cuts. From Ran, et al. (2013). |
Applications for genome editing
Because genome editing begins with DSBs, many applications are possible. The most common is gene knockout. At the simplest level, either a TALEN pair, or the combination of the Cas9 nuclease with a single guide RNA, creates a DSB, leading to error-prone repair. Occasionally, small insertions occur, but NHEJ more commonly results in the formation of small deletions of varying lengths (Figure 3).
| Figure 4. TALEN activity leads to target site-specific insertions or deletions. From Wang, et al. (2013).
The frequencies of frameshifts vary widely, influenced by the particular TALEN pair or CRISPR sgRNA. Reports in the literature of efficiencies, as measured by the percentage of cell line clones carrying a mutation, range from 0% to more than 70%. |
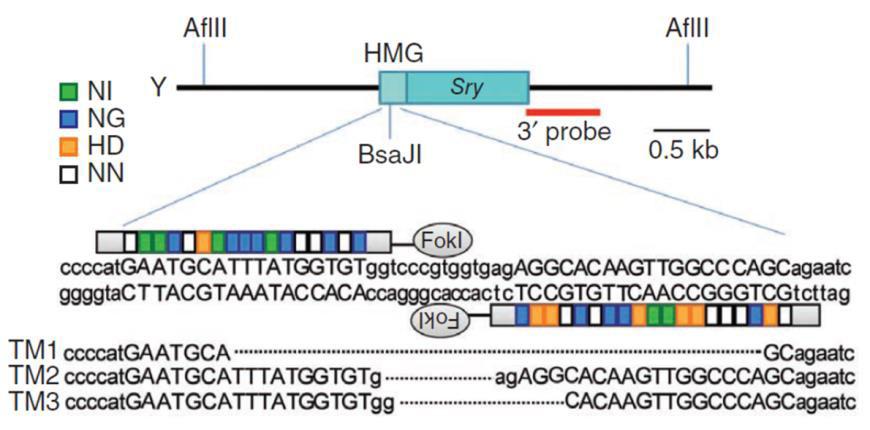
Knockouts can also be achieved with a homologous donor (Figure 5). In the simplest case, the sgRNA is designed to cut in the earliest protein-coding region in common to all splice variants. It can be the same target sequence as that used for donorless knockouts. The donor is constructed such that insertion of a selection/reporter cassette causes a deletion in the sgRNA binding site, to both knock the gene out and simultaneously prevent cleavage of the donor. The donor is co-introduced with the Cas9/sgRNAs. 2-3 days post-transfection, selection for the drug resistance gene in the donor (e.g. puromycin) is applied, single drug-resistant colonies are identified, and then screened for the correct insertions.
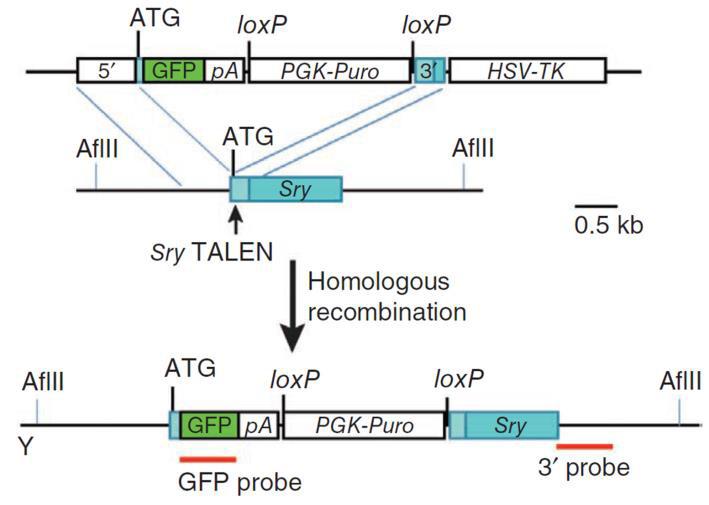
|
Figure 5. Knockout of the mouse Sry gene using a donor plasmid. Top. Donor plasmid consisting of a cassette with GFP and a puromycin resistance gene. The cassette is flanked by sequences homologous to the mouse Sry target region. The clone is designed such that the cassette is inserted between the initiator ATG and the rest of the gene. Bottom. Co-introduction of a TALEN with the donor plasmid causes recombination between the donor and the Sry locus, leading to replacement of the endogenous sequences with the sequence interrupted by the cassette and knockout of the gene. From Wang, et al. (2013) |
GeneCopoeia carries all the reagents necessary for customers to knock their genes out, by either NHEJ- mediated indels, or with a donor clone. These include clones expressing TALEN pairs or sgRNAs targeted to a region if interest, Cas9 clones, and donor clones built for knockout as well as other applications. Our CRISPR clones come in non-viral and lentiviral format, for hard-to-transfect cell lines.
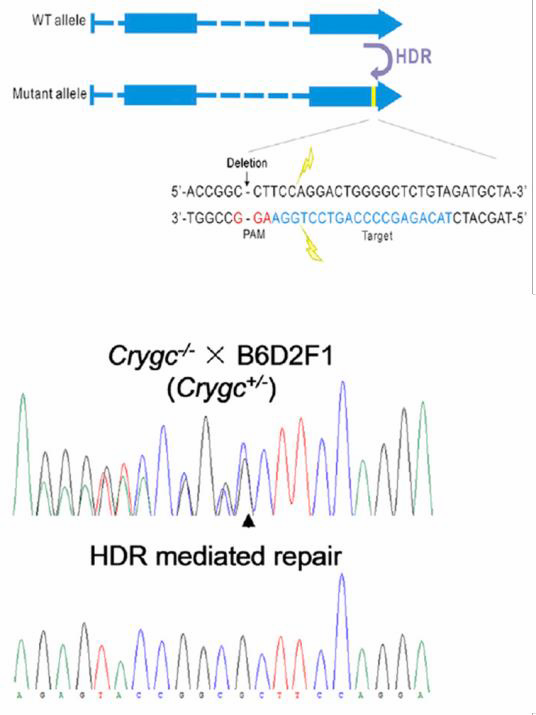
| Figure 6. Curing of heritable cataract disorder using CRISPR
and an ssODN in transgenic mice. From Wu, et al. (2013)
Other genome editing applications require a homologous donor. One is introduction of a single base change, which can be achieved using a donor plasmid or a single strand oligonucleotide (ssODN). In the ssODN strategy, an oligonucleotide carries the base change and 40-90 nucleotides of homology flanking the target region. The method works with high efficiency. Jinsong Li’s lab used CRISPR with an ssODN to correct a single base mutation that causes cataracts in mice (Wu, et al., 2013; Figure 6). |
Both TALEN and CRISPR are highly effective technologies for genome editing. Each, however, has its limitations, and these factors need to be taken into account when choosing one technology over the other. On one hand, TALEN is sensitive to cytosine methylation, and so a methyl C-specific RVD must be designed for recognition. CRISPR, though, is not methylation- sensitive. In addition, TALEN cutting efficiency tends to be lower than CRISPR’s. On the other hand, TALEN tends to be less prone to off-target mutagenesis than CRISPR, although recent improvements in the technology, such as the use of double nickases, truncated guide RNAs, and a Cas9-Fok I fusion, improve CRISPR target site specificity.
Conclusions
At GeneCopoeia, we provide a full suite of genome editing products and services. These begin with TALEN and CRISPR clone design and construction, but our expertise doesn’t stop there. We also offer functional validation of TALEN and CRISPR clones. In addition, we will construct both stable cell lines and transgenic mice carrying your modification of interest. From our long-standing expertise in mammalian ORF and promoter clones, we have built a database of more than 40,000 knockout targets for human and mouse, which can be conveniently purchased from our website. Our experts can also help you with demanding custom genome editing applications. Contact us today at inquiry@genecopoeia.com! For more information, please visit our Genome Editing page: https://www.genecopoeia.com/product/genome-editing/References
Bogdanove & Voytas (2011). Science 333, 1843. Ran, et al. (2013). Nature Protocols 8, 2281. van der Oost, et al. (2013). Science 339, 768. Wang, et al. (2013). Nature Biotech. 31, 530. Wang, et al. (2014). Science 343, 80. Wu, et al. (2013). Cell Stem Cell 13, 659.| Copyright ©2014 GeneCopoeia, Inc. www.genecopoeia.com RAGE1-080614 |
